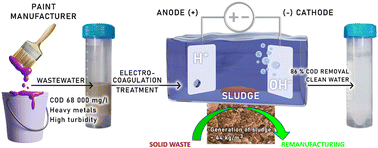
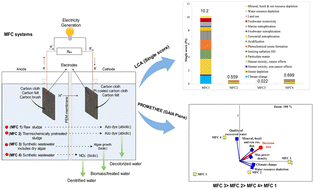
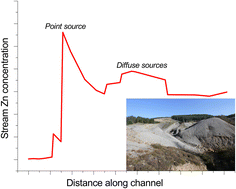
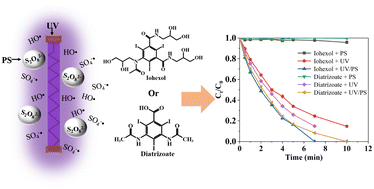
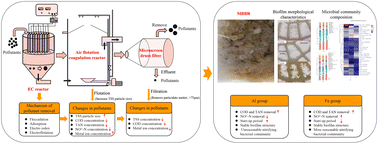
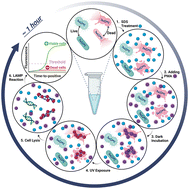
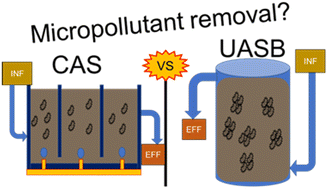
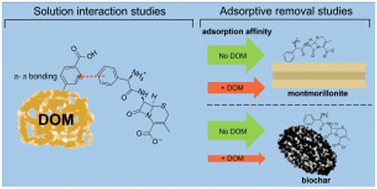
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024, 10,652-667
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00784G, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00784G, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Sara Feijoo, Simona Baluchová, Mohammadreza Kamali, Josephus G. Buijnsters, Raf Dewil
Understanding electrochemical oxidation mechanisms through a combined experimental and computational approach.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Understanding electrochemical oxidation mechanisms through a combined experimental and computational approach.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry