Energy Adv., 2023, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3YA00336A, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3YA00336A, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Faezeh Makhlooghiazad, Colin S. M. Kang, Mojtaba Eftekharnia, Patrick C. Howlett, Oliver Hutt, Maria Forsyth, Luke A. O’Dell, Jennifer M. Pringle
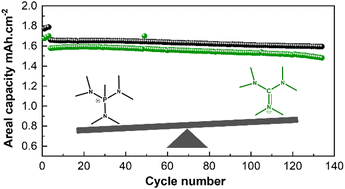
Two high-salt-content ionic liquid electrolytes with distinct cationic chemistries were compared. The one with a phosphonium cation showed superior characteristics, particularly in terms of its enhanced capacity when used in lithium metal batteries.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Two high-salt-content ionic liquid electrolytes with distinct cationic chemistries were compared. The one with a phosphonium cation showed superior characteristics, particularly in terms of its enhanced capacity when used in lithium metal batteries.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry