Environ. Sci.: Adv., 2024, 3,355-365
DOI: 10.1039/D3VA00176H, Communication
DOI: 10.1039/D3VA00176H, Communication
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence.Milena Esser, Phillip Ankley, Caroline Aubry-Wake, Yuwei Xie, Helen Baulch, Cameron Hoggarth, Markus Hecker, Henner Hollert, John P. Giesy, John W. Pomeroy, Markus Brinkmann
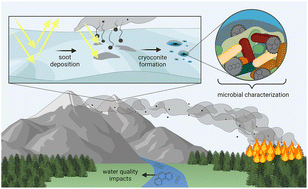
Glacier ecosystems are shrinking at an accelerating rate due to changes in climate, and increased darkening from allochthonous and autochthonous carbon is leading to changes in light absorption, associated heat, and microbial communities.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Glacier ecosystems are shrinking at an accelerating rate due to changes in climate, and increased darkening from allochthonous and autochthonous carbon is leading to changes in light absorption, associated heat, and microbial communities.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry