Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2023, 3,1460-1484
DOI: 10.1039/D3EA00102D, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EA00102D, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Nathan A. I. Watson, Joseph M. Beames
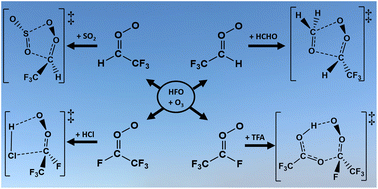
When haloalkene refrigerants break down, this study shows that the resultant halogenated Criegee intermediates have an enhanced capacity to deplete many gaseous pollutants (e.g. HCHO & SO2) but also produce atmospheric contaminants (e.g. SO3 & TFA).
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
When haloalkene refrigerants break down, this study shows that the resultant halogenated Criegee intermediates have an enhanced capacity to deplete many gaseous pollutants (e.g. HCHO & SO2) but also produce atmospheric contaminants (e.g. SO3 & TFA).
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry