Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3EM00405H, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EM00405H, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Philip T. Gidley, Guilherme R. Lotufo, Stine N. Schmidt, Philipp Mayer, Robert M. Burgess
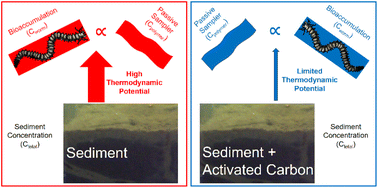
Compared to untreated polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) contaminated sediments, activated carbon amendment to sediment reduced the thermodynamic potential for bioaccumulation and proportional partitioning-based sampling uptake.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Compared to untreated polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) contaminated sediments, activated carbon amendment to sediment reduced the thermodynamic potential for bioaccumulation and proportional partitioning-based sampling uptake.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry