Catal. Sci. Technol., 2023, 13,5757-5766
DOI: 10.1039/D3CY00606A, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3CY00606A, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Reina Kaneda, José Palomo, Lingjun Hu, Atsushi Urakawa
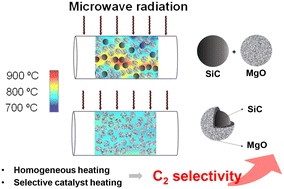
The oxidative coupling of methane (OCM) was investigated using a catalyst with a core@shell structure or a physical mixture comprised of MgO and SiC or Fe3O4, which was thermally activated via conventional resistive heating or microwave heating.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
The oxidative coupling of methane (OCM) was investigated using a catalyst with a core@shell structure or a physical mixture comprised of MgO and SiC or Fe3O4, which was thermally activated via conventional resistive heating or microwave heating.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry