Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2023, 3,1485-1496
DOI: 10.1039/D3EA00082F, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EA00082F, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence.Vianni G. Straccia C., María B. Blanco, Mariano A. Teruel
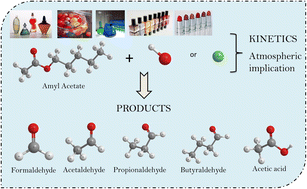
When hydrogenated esters are released into the atmosphere, they may be oxidized by OH radicals and Cl atoms, forming aldehydes and acids that have a negative local, regional, and worldwide environmental impact.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
When hydrogenated esters are released into the atmosphere, they may be oxidized by OH radicals and Cl atoms, forming aldehydes and acids that have a negative local, regional, and worldwide environmental impact.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry