Biomater. Sci., 2023, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3BM00917C, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3BM00917C, Paper
Sung Jin Kim, Ui Joung Youn, Pilsung Kang, Tai Kyoung Kim, Il-Chan Kim, Se Jong Han, Dong-Woo Lee, Joung Han Yim
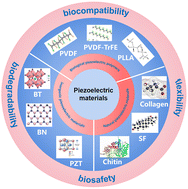
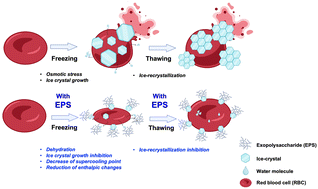
A novel EPS (p-CY01), derived from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain CY01, can serve as a non-penetrating cryopreservation agent for the long-term storage of human red blood cells.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
A novel EPS (p-CY01), derived from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain CY01, can serve as a non-penetrating cryopreservation agent for the long-term storage of human red blood cells.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

 Open Access
Open Access