Biomater. Sci., 2023, 11,6619-6634
DOI: 10.1039/D3BM01265D, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3BM01265D, Paper
Zixu Liu, Linxuan Zhao, Yupeng Feng, Qingqing Wang, Nan Dong, Yu Zhang, Tian Yin, Haibing He, Xing Tang, Jingxin Gou, Li Yang
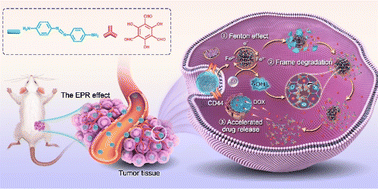
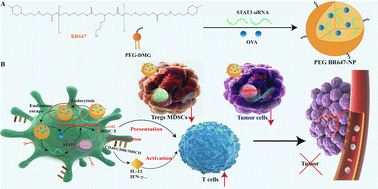
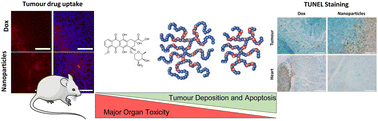
Dual-responsive PEG-lipid polyester nanoparticles (PEG BR647-NPs) were employed as a vaccine and STAT3 siRNA carrier for tumor-targeted delivery to modulate the tumor microenvironment.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Dual-responsive PEG-lipid polyester nanoparticles (PEG BR647-NPs) were employed as a vaccine and STAT3 siRNA carrier for tumor-targeted delivery to modulate the tumor microenvironment.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

 Open Access
Open Access