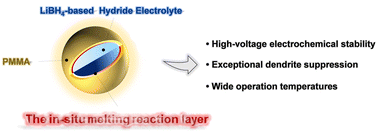
Energy Environ. Sci., 2023, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3EE01471A, Perspective
DOI: 10.1039/D3EE01471A, Perspective
Prince Aleta, Abdelrahman Refaie, Mohsen Afshari, Ahmad Hassan, Mohammad Rahimi
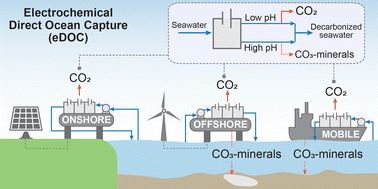
This study explores the emerging development of electrochemical direct ocean capture (eDOC) as an effective negative emission technology; focusing on pH swing mechanisms, we highlight advancements in eDOC and identify key areas for future research.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
This study explores the emerging development of electrochemical direct ocean capture (eDOC) as an effective negative emission technology; focusing on pH swing mechanisms, we highlight advancements in eDOC and identify key areas for future research.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

 Open Access
Open Access