Faraday Discuss., 2023, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3FD00114H, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3FD00114H, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Aditya Limaye, Dylan Suvlu, Adam P. Willard
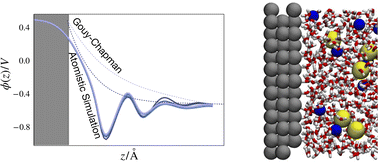
We study the effects of changing electrolyte concentration on interfacial potential profiles, specifically comparing the predictions of continuum-level theory and all-atom molecular dynamics simulation.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
We study the effects of changing electrolyte concentration on interfacial potential profiles, specifically comparing the predictions of continuum-level theory and all-atom molecular dynamics simulation.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry