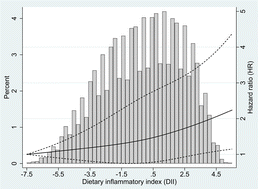
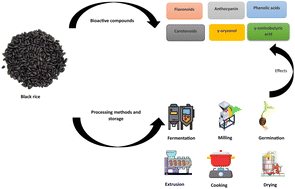
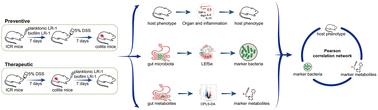
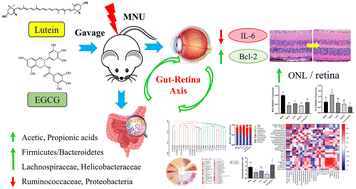
Food Funct., 2023, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3FO02605A, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3FO02605A, Paper
Hang Liu, Jiawen Song, Lei Zhou, Shengfeng Peng, David Julian McClements, Wei Liu
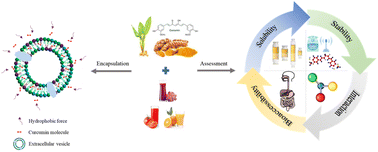
Different fruit and vegetable juices were first used to encapsulate curcumin to improve its solubility, stability, and bioaccessibility, which is expected to enable designing of polyphenol-enriched beverages and have an impact on human health and well-being.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Different fruit and vegetable juices were first used to encapsulate curcumin to improve its solubility, stability, and bioaccessibility, which is expected to enable designing of polyphenol-enriched beverages and have an impact on human health and well-being.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

 Open Access
Open Access