Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024, 26,411-420
DOI: 10.1039/D3EM00354J, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EM00354J, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence.Lu Zhou, Thibault Masset, Florian Breider
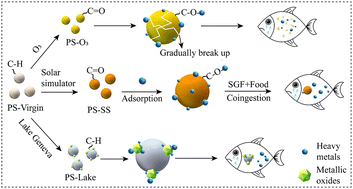
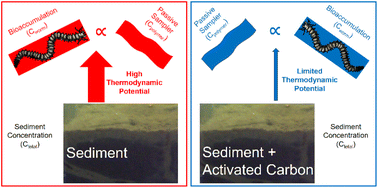
Microplastics, especially aged microplastics can become vectors of metals from environment to organisms with potential negative effects on food chain.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Microplastics, especially aged microplastics can become vectors of metals from environment to organisms with potential negative effects on food chain.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry