Faraday Discuss., 2023, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3FD00109A, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3FD00109A, Paper
Roger John-Erik Reinertsen, Felipe Jiménez-Ángeles, Sumit Kewalramani, Michael Bedzyk, Monica Olvera de la Cruz
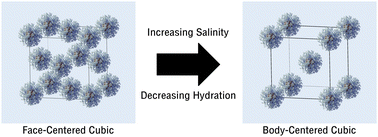
Colloidal crystals of DNA-coated nanoparticles transition from face-centered cubic to body-centered cubic structures with increasing salinity; this transition is concurrent with salt-induced dehydration of the grafted DNA.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Colloidal crystals of DNA-coated nanoparticles transition from face-centered cubic to body-centered cubic structures with increasing salinity; this transition is concurrent with salt-induced dehydration of the grafted DNA.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

 Open Access
Open Access