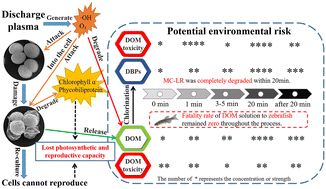
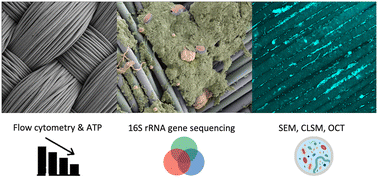
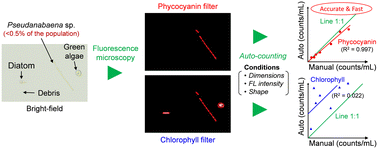
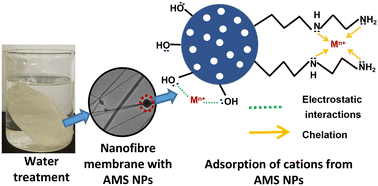
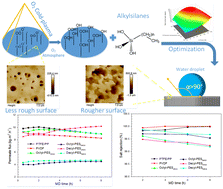
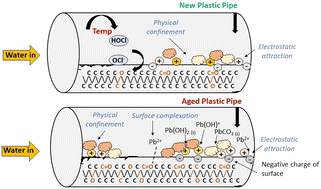
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023, 9,2569-2580
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00198A, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00198A, Paper
Chad Verwold, Christopher Tremblay, Miriam Patron, Susana Y. Kimura
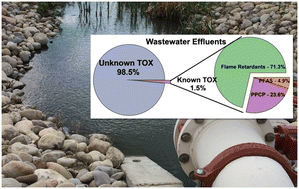
A total organic halogen method for wastewater was developed and compared with target methods where only 1.5% of TOX was known.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
A total organic halogen method for wastewater was developed and compared with target methods where only 1.5% of TOX was known.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

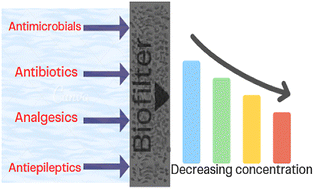
 Open Access
Open Access