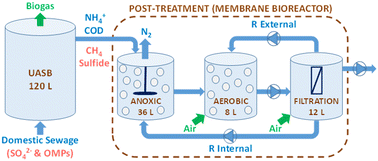
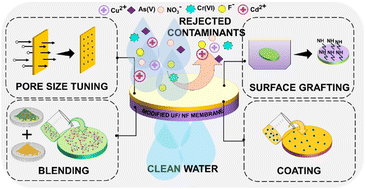
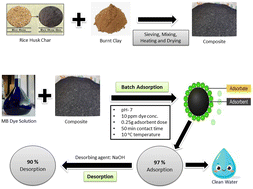
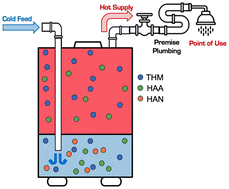
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023, 9,2692-2705
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00327B, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00327B, Paper
Harshit Tiwari, Sanjeev Kumar Prajapati
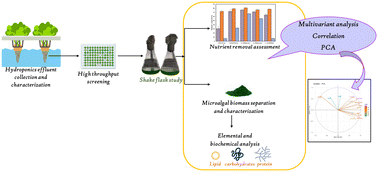
Here we comparatively assessed eight different microalgae for possible recycling and bioconversion of residual nutrients from hydroponic effluent (HE) into biochemical-rich microalgal biomass.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Here we comparatively assessed eight different microalgae for possible recycling and bioconversion of residual nutrients from hydroponic effluent (HE) into biochemical-rich microalgal biomass.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

 Open Access
Open Access