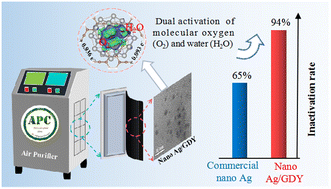
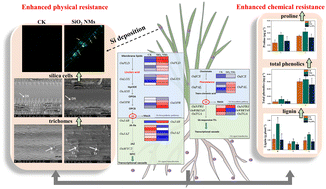
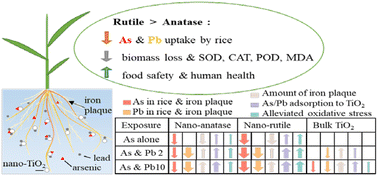
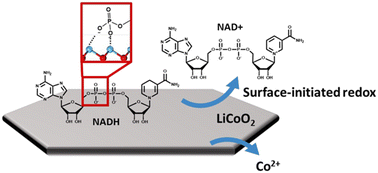
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023, 10,2890-2903
DOI: 10.1039/D3EN00268C, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EN00268C, Paper
Gregory M. Newkirk, Su-Ji Jeon, Hye-In Kim, Supreetha Sivaraj, Pedro De Allende, Christopher Castillo, Robert E. Jinkerson, Juan Pablo Giraldo
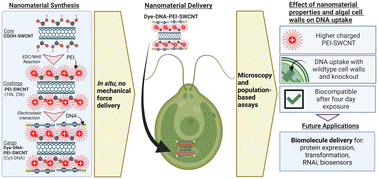
Single walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are coated with polyethylenimine (PEI) of different molecular weight for DNA delivery into algal chloroplasts without the use of mechanical aid for understanding their impact on cell viability and function.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Single walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are coated with polyethylenimine (PEI) of different molecular weight for DNA delivery into algal chloroplasts without the use of mechanical aid for understanding their impact on cell viability and function.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

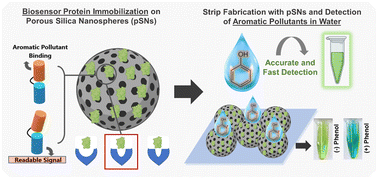
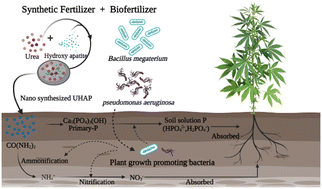
 Open Access
Open Access