Digital Discovery, 2023, 2,1368-1379
DOI: 10.1039/D3DD00030C, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3DD00030C, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Noah Hoffmann, Jonathan Schmidt, Silvana Botti, Miguel A. L. Marques
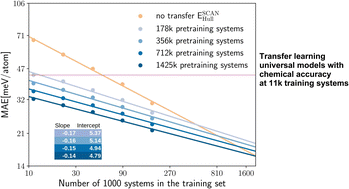
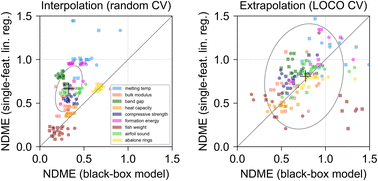
Pretraining on large, lower-fidelity datasets enables extremely effective training of graph neural networks on smaller, high-fidelity datasets.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Pretraining on large, lower-fidelity datasets enables extremely effective training of graph neural networks on smaller, high-fidelity datasets.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry