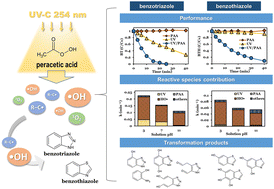
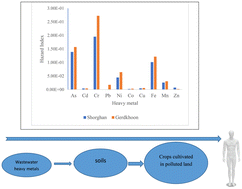
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00867C, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D3EW00867C, Paper
M. Martin, Jingyi Wu, Stephanie L. Rich, Ruth E. Richardson, Damian E. Helbling
We report differential micropollutant biotransformations in a conventional activated sludge (CAS) process and a pilot-scale up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) process operating in parallel at the same wastewater treatment plant.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
We report differential micropollutant biotransformations in a conventional activated sludge (CAS) process and a pilot-scale up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) process operating in parallel at the same wastewater treatment plant.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

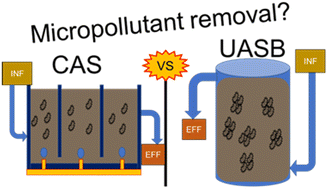
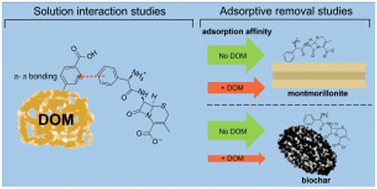
 Open Access
Open Access